This 56 minute PBS broadcast, The Wings of Angels, describes in general audience terms what I now believe has always been the fundamental basis of politics for as long as humans have been doing politics. In essence, politics is a struggle or competition for power, wealth and advantage. The struggle plays out between at least two fundamentally different but not always completely separate human mindsets, cooperative-democratic and competitive-authoritarian. The struggle plays out in the human mind mostly (~97% ?) unconsciously, emotional, intuitive, moral and social, not consciously and rational. Because of that, the human mind is easily hackable and governments, businesses and religions have all developed effective ways to hack our minds.
The program poses the question of whether democracies should consciously engage in mind hacking for good, at least in part as defense against the all-out hacking war that some authoritarian governments, most prominently China, now use to subdue their people and quash dissent, all with the unconscious cooperation of the subjugated people. China present a possible model for the ultimate fate of the human species, eternal enslavement and oppression.
Wings of Angels is the third in a series of three called
Hacking Your Mind that PBS produced about the workings of the human mind and what modern cognitive and social science now understand the human condition to be. This program is mind blowing. It is akin to the Netflix documentary
Social Dilemma. It is another sign that the incredible importance of modern cognitive and social science in understanding the human condition, politics and everything else about humans.
My description of mind hacking
Mind hacking happens all the time. People engage in behavior that influences the behavior of others. That happens by shaping the reality others see, e.g., by experiencing a person’s (hacker’s) behaviors, including speech, and unconsciously reacting to it. Whether hacking is intended or not, various behaviors affect the observer’s mental state, cognitive processes and/or level of cognitive function. In politics, there usually is (~99% of the time?) intent to manipulate the target audience’s behavior without their knowledge or consent. That said, people mind hack by simply being alive and interacting with other people. That cannot be helped or changed because it is an inherent, fundamental trait of the human mind. For politics, the main question is whether the hacking is for authoritarianism and the dictator’s vision of law and order, or for messy, chaotic democracy.
Key points
For those who don't want to take the time to watch this, these three points stand out.
Point #1: Whether we like it or want it or not, we are all mind hackers. Simply being alive and interacting with others hacks minds. This blog post hacks minds, but at least the intent is for good, not bad.
Wings of Angels poses the question should we hack in a democracy. But the question is moot. We do hack, whether we like or want it or not. Some people argue a slippery slope will lead democracy into tyranny if we do mind hack. That argument is not accompanied by a recognition of two key points.
First, there may be a worse slippery slope if we do not hack for good because authoritarians hack their people. Mind hacked authoritarianism could come to dominate the entire human species for thousands of years. In my opinion, it is the most plausible means to enslave the human race forever.[1] Wings of Angels makes that point clear in its discussion of how Chinese authoritarians now effectively employ mind hacking to get the Chinese people to willingly but unknowingly support their own tyranny by suppressing dissent and ‘bad citizenship’. The Chinese voluntary opt-in mind hack tactic is brilliant, brutal and effective.
Second, mind hacking is multidirectional. It can be for good, bad, stupid, entertainment, educating, disinforming, ethnic cleansing, waging war, saving a marriage, picking better musicians for an orchestra, reducing criminal recidivism, selling anything (smart or dumb, useful or useless, e.g., pet rocks) to consumers or just about anything else.
Chinese people voluntarily opt-in to a social monitoring and
grading system that monitors and punishes bad citizens and
rewards good ones -- essentially everything is monitored 24/7/365
(my guess is that most opt in due mostly to a combination of social
pressure and a predisposing collective culture mindset)
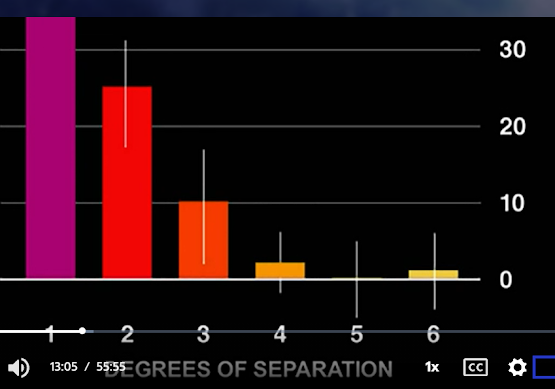
Point #2: Mind hacking can have amazing subtlety, power and social reach. It is a true
social contagion phenomenon. It can reach past degrees of separation and right through to people's minds and behaviors in ways that profoundly affect other minds and behaviors. This happens without one shred of awareness of any of the people involved.
The Wings of Angels discusses research on obese people, their friends, friends of their friends and so on.
In that research, being obese was shown to reach through to a person separated by at least 3 degrees of separation. The data indicated that an obese friend (1st degree) of an obese friend (2nd degree) of an obese person (3rd degree) can influence whether a person tends to be obese merely by association with the 1st degree friend. That happens without the person even knowing the 2nd or 3rd degree persons exist at all. Something is transmitted from the 3rd degree person all the way to the affected person and no one has any idea that it is happening. The same observation is found with alcohol drinking.
1st degree of separation = friend of a mind hacked person
2nd degree = friend of the friend of the mind hacked person
3rd degree = friend of the friend of the friend of the mind hacked person
4th degree = etc.
If there is any at least partly effective vaccine to this social contagion phenomenon, it lies in teaching self-awareness and critical thinking skills.
Point #3: Lastly, pro-environmental mind hacking research shows that appealing to conscious reason fails, but appealing to the unconscious mind can work quite well. This research harks back to observations on the human condition by the eccentric economist-satirist Thorstein Veblen, some of which are described in his strange, brilliant 1899 book,
The Theory of the Leisure Class. In short, when one keeps up with the Jonses, one has usually been mind hacked. If Jones buys a Buick, you buy a Buick or preferably a Cadillac or BMW. That's a mind hack. In this situation, at least some people are probably aware to some extent that they are keeping up with the Jonses, but they aren't aware they have been mind hacked.
The research looked for ways to get people to be more energy efficient, e.g., by using less energy and having lower utility bills. Three groups received one of three different appeals to conscious reason, e.g. it will lower your energy bills or your children will be better off if the environment is not so polluted. Once group was mind hacked by appeal to what the Jonses do. The mind hack group was simply shown how much energy their household used compared to their neighbors (the Jonses) and told nothing else.
The result? Only the mind hack group showed a significant energy use drop. The other groups did not change in their energy consumption. Based on that research, appeals to slow, weak conscious reason to help the environment failed, but appeals to the fast powerful unconscious mind succeeded. If that research is replicated and holds up, this observation reflects the core messages that Nobel laureate Daniel Khaneman described in his well-known 2012 book,
Thinking, Fast and Slow, and what psychologist Johnathan Haidt described in his 2012 book,
The Righteous Mind: Why Good People are Divided by Politics and Religion.
Questions:
Should our government use mind hacks to better serve the public interest, or is it too dangerous?
Did Obama make a mistake when he opened a federal office dedicated to applying behavioral science to federal policy when possible?
Footnote:
1. Most plausible because it is the political “ideology” most based on what the human mind is and how it works according to modern science. Science-based political ideology transcends liberalism, conservatism, Christianity, capitalism, socialism, fascism, racism and all the other significant ideologies in politics that I am aware of in terms of effectiveness. To the best of my knowledge, only
pragmatic rationalism (PR) can
potentially come close to what the Chinese government has done and is doing (Only potential because it is not a significant political ideology and the hypothesis remains untested). That is because PR is also based on the science of the human mind. PR, like the Chinese counterpart, rational authoritarianism(?), tries to understand and accept humans for what they are, not for what they ought to be according to any ideology that is unduly detached from relevant science.
The Wings of Angels points out that the short 2009 book
Nudge: Improving Decisions About Health, Wealth and Happiness, a book by Richard Thaler and Cass Sunstein was highly influential in shaping Chinese government thinking about how to control its people.
Thaler's work earned him a Nobel prize in 2015 in behavioral economics for his understanding that humans are not the rational creatures that obey the complex equations that economists falsely believed they obey. The Chinese are dead serious about using cognitive and social science to inform their brilliant mind hacking tactics.
I've posted several times about the growing Chinese authoritarian cognitive mind hack technology and its underlying foundation in advanced, all-encompassing deep surveillance technology. For example, the Chinese government uses it for
ethnic cleansing and
reinforcing good citizenship as the dictators explicitly define good citizenship and grade people on. The lives of bad citizens are forced into misery, low income and low social status. Who knows, maybe they go extinct.